Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Problems before Docker:-
A developer develops and runs an application. Now that application works in developer’s laptop but not in testing or production. This problem is arised due to difference in computing environment between developer, test and production team. In development environment there can be a software that is upgraded and in testing and production environment, the older version of software might be present.
What is Docker?
Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Docker containers are lightweight alternatives to Virtual Machines and it uses the host OS. You don't have to pre-allocate any RAM in containers.
Dockerfile builds a docker image and that image contains all the project's code. You can run that image to create as many docker containers as you want. Then this image can be uploaded on DockerHub, from DockerHub anyone can pull the image and build a container.
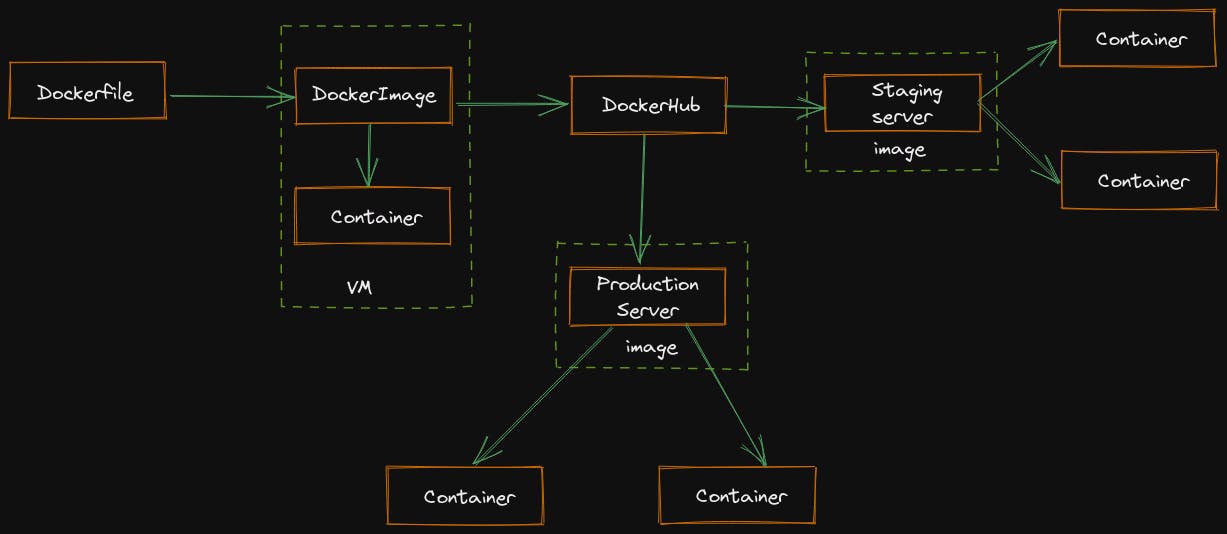
Docker images are huge in size and requires a lot of network bandwidth. So in order to save that network bandwidth, we use Jenkins server or any continuous integration server to build an environment that contains all the dependencies for a particular application or a microservice and that build environment is deployed onto various teams like testing, staging and production.
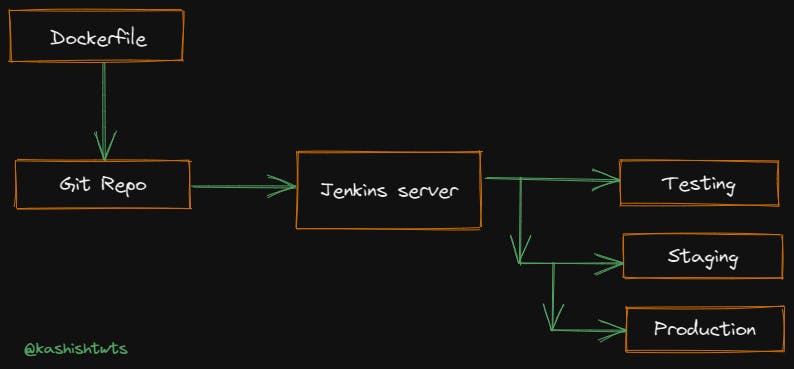 Create complex requirements for a microservice within an easy-to-write Dockerfile. Then push the code to the Git repository. CI server pull it down and build the exact environment that will be used in production to run the test suite without needing to configure the CI server at all. Deploy it out to a staging environment for testers. Roll exactly what you had in development, testing, and staging into production.
Create complex requirements for a microservice within an easy-to-write Dockerfile. Then push the code to the Git repository. CI server pull it down and build the exact environment that will be used in production to run the test suite without needing to configure the CI server at all. Deploy it out to a staging environment for testers. Roll exactly what you had in development, testing, and staging into production.
What is Docker registry?
Docker registry is a storage component for Docker images. We can store the images in either public or private repositories. DockerHub is famous public cloud repository.
Why use Docker Registries?
You can control where your images are being stored. Integrate image storage with your in-house development workflow.
What are Docker images?
Docker images are read only template that can be used to create containers out of it. These docker images contains all the dependencies for a particular application or any microservice. You can create your own image and upload that onto the DockerHub and at the same time you can also pull the images which are available in the public repositories.
What are Docker containers?
Docker containers are nothing but the runtime instances of docker images. It contains everthing that is required to run an application or any microservice. It is also possible that more than one image is required to create a container. Docker containers can be referred to as isolated application platform built from one or more docker images.
Docker compose
Suppose you have multiple applications on various containers and all those containers are linked together. So you don’t want to actually execute each of those containers one by one but want to run those containers at once with a single command. So here docker compose comes into picture.
Docker compose makes it easier to configure and run applications made up of multiple containers. For example, you define four containers in one YAML file and then run those four containers with a single command.

That's it for this one.
Thanks for reading!
Any feedbacks are welcome!!


